Hedging strategies stock options
Hedging is the practice of purchasing and holding securities specifically to reduce portfolio risk. These securities are intended to move in a different direction than the remainder of the portfolio - for example, appreciating when other investments decline.
A put option on a stock or index is the classic hedging instrument. When properly done, hedging significantly reduces the uncertainty and the amount of capital at risk in an investment, without significantly reducing the potential rate of return. How It's Done Hedging may sound like a cautious approach to investing, destined to provide sub-market returns, but it is often the most aggressive investors who hedge.
By reducing the risk in one part of a portfolio, an investor can often take on more risk elsewhere, increasing his or her absolute returns while putting less capital at risk in each individual investment. Hedging is also used to help ensure that investors can meet future repayment obligations.
For example, if an investment is made with borrowed money, a hedge should be in place to make sure that the debt can be repaid. Or, if a pension fund has future liabilities, then it is only responsible for hedging the portfolio against catastrophic loss. Downside Risk The pricing of hedging instruments is related to the potential downside risk in the underlying security.
As a rule, the more downside risk the purchaser of the hedge seeks to transfer to the seller , the more expensive the hedge will be.
Downside risk, and consequently option pricing, is primarily a function of time and volatility.
The reasoning is that if a security is capable of significant price movements on a daily basis, then an option on that security that expires weeks, months or years in the future will be highly risky, and therefore, costly. On the other hand, if the security is relatively stable on a daily basis, there is less downside risk, and the option will be less expensive.
This is why correlated securities are sometimes used for hedging. If an individual small cap stock is too volatile to hedge affordably, an investor could hedge with the Russell , a small cap index, instead.
The strike price of a put option represents the amount of risk that the seller takes on. Options with higher strike prices are more expensive, but also provide more price protection.
Of course, at some point, purchasing additional protection is no longer cost effective. In the example, buying puts at higher strike prices results in less capital at risk in the investment, but pushes the overall investment return downward.
Pricing Theory and Practice In theory, a perfectly priced hedge, such as a put option, would be a zero-sum transaction. The purchase price of the put option would be exactly equal to the expected downside risk of the underlying security. However, if this were the case, there would be little reason not to hedge any investment. Of course, the market is nowhere near that efficient, precise or generous. The reality is that most of the time and for most securities, put options are depreciating securities with negative average payouts.
There are three factors at work here:. The Importance Of Time Value and Risk Graphs: Visualizing Your Profit Potential. Because the expected payout of a put option is less than the cost, the challenge for investors is to only buy as much protection as they need. This generally means purchasing puts at lower strike prices and assuming the security's initial downside risk.

Spread Hedging Index investors are often more concerned with hedging against moderate price declines than severe declines, as these type of price drops are both very unpredictable and relatively common.
For these investors, a bear put spread can be a cost-effective solution. In a bear put spread, the investor buys a put with a higher strike price and then sells one with a lower price with the same expiration date. Note that this only provides limited protection, as the maximum payout is the difference between the two strike prices.
However, this is often enough protection to handle a mild-to-moderate downturn. Note that options on IWM are penny priced and highly liquid. Time Extension and Put Rolling Another way to get the most value out of a hedge is to purchase the longest available put option.
When purchasing any option, the marginal cost of each additional month is lower than the last. In the above example, the most expensive option for a long-term investor also provides him or her with the least expensive protection per day. This also means that put options can be extended very cost effectively.
If an investor has a six-month put option on a security with a certain strike price, it can be sold and replaced with a month option at the same strike.
This can be done over and over again. The practice is called rolling a put option forward. By rolling a put option forward and keeping the strike price close to, but still somewhat below, the market price , an investor can maintain a hedge for many years. This is very useful in conjunction with risky leveraged investments like index futures or synthetic stock positions. Calendar Spreads The diminishing cost of adding extra months to a put option also creates an opportunity to use calendar spreads to put a cheap hedge in place at a future date.
Calendar spreads are created by purchasing a long-term put option and selling a shorter-term put option at the same strike price. The danger is that the investor's downside risk is unchanged for the moment, and if the stock price declines significantly in the next few months, the investor may face some difficult decisions.
Should he or she exercise the long put and lose its remaining time value? Or should the investor buy back the short put and risk tying up even more money in a losing position?
In favorable circumstances, a calendar put spread can result in a cheap long-term hedge that can then be rolled forward indefinitely. However, investors need to think through the scenarios very carefully to ensure that they don't inadvertently introduce new risks into their investment portfolios. The Bottom Line Hedging can be viewed as the transfer of unacceptable risk from a portfolio manager to an insurer.
This makes the process a two-step approach. First, determine what level of risk is acceptable. Then, identify the transactions that can cost effectively transfer this risk. As a rule, longer term put options with a lower strike price provide the best hedging value.
Options strategies - Wikipedia
They are initially expensive, but their cost per market day can be very low, which makes them useful for long-term investments. These long-term put options can be rolled forward to later expiries and higher strike prices, ensuring that an appropriate hedge is always in place.
Some investments are much easier to hedge than others. Usually, investments such as broad indexes are much cheaper to hedge than individual stocks. Lower volatility makes the put options less expensive, and a high liquidity makes spread transactions possible. But while hedging can help eliminate the risk of a sudden price decline, it does nothing to prevent long-term underperformance. It should be considered a complement , rather than a substitute, to other portfolio management techniques such as diversification , rebalancing and disciplined security analysis and selection.

Dictionary Term Of The Day. A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund. Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin?
This Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam. Sophisticated content for financial advisors around investment strategies, industry trends, and advisor education.
Practical And Affordable Hedging Strategies By Tristan Yates Share. A Beginner's Guide To Hedging Downside Risk The pricing of hedging instruments is related to the potential downside risk in the underlying security.
Options Basics Pricing Theory and Practice In theory, a perfectly priced hedge, such as a put option, would be a zero-sum transaction.
There are three factors at work here: Volatility Premium - As a rule, implied volatility is usually higher than realized volatility for most securities, most of the time. Why this happens is still open to considerable academic debate, but the result is that investors regularly overpay for downside protection.
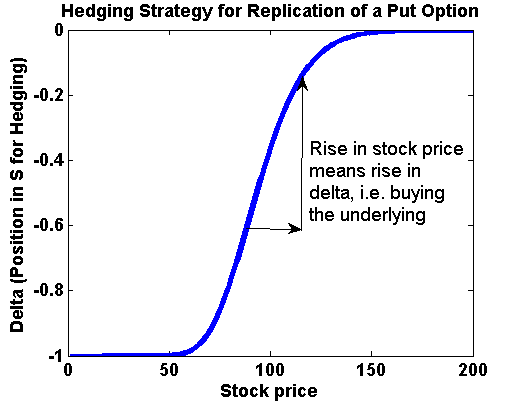
Index Drift - Equity indexes and associated stock prices have a tendency to move upward over time. This gradual increase in the value of the underlying security results in a decline in the value of the related put.
Time Decay - Like all long option positions, every day that an option moves closer to expiry, it loses some of its value. The rate of decay increases as the time left on the option decreases. Visualizing Your Profit Potential Because the expected payout of a put option is less than the cost, the challenge for investors is to only buy as much protection as they need.
Option Spread Strategies In a bear put spread, the investor buys a put with a higher strike price and then sells one with a lower price with the same expiration date.
Example - Bear Put Spread Strategy IWM , the Russell ETF, trades for Example - Buying a Long-Term Put Option Available put options on IWM, trading at This trading strategy can reduce your risk - but only if you use it effectively.
This strategy is widely misunderstood, but it's not as complicated as you may think. A brief overview of how to profit from using put options in your portfolio. Options offer alternative strategies for investors to profit from trading underlying securities, provided the beginner understands the pros and cons.
Hedging Strategies - Balancing Your Stock or Options Portfolio
Proper hedges help to contain your losses while still allowing profits to grow. The adage "know thyself"--and thy risk tolerance, thy underlying, and thy markets--applies to options trading if you want it to do it profitably. Learn about different hedging strategies to reduce portfolio volatility and risk, including diversification, index options Learn how using an out-of-the-money time put spread can be used to hedge downside risk by reducing the amount of premium Learn about option strategies used to hedge a long stock position in the telecommunications sector, including bear put spreads Learn about one of the most common risk-management strategies options traders use, called spread hedging, to limit exposure Learn about put options, considerations to make before you select strike prices and how to select strike prices for your Learn about put options, what they are, how these financial derivatives operate and when put options are considered to be An expense ratio is determined through an annual A hybrid of debt and equity financing that is typically used to finance the expansion of existing companies.
A period of time in which all factors of production and costs are variable. In the long run, firms are able to adjust all A legal agreement created by the courts between two parties who did not have a previous obligation to each other.
A macroeconomic theory to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between rising wages and rising prices, or inflation. A statistical technique used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over No thanks, I prefer not making money. Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator.
Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers.
Option { CE & PE } Writing With Hedging strategies In Stock Market [ HINDI ]Get Free Newsletters Newsletters. All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy. IWM is the Russell tracker ETF Strike.