Forex market structure pdf
For most retail traders understanding the structure of the Forex market is something that is often overlooked. This is a critical element that needs to be considered when designing and implementing any trading plan.
The forex market differs from other global markets due to the way it is structured. The main factors affecting the structure of the Forex market are the ways Forex products are traded, the participants and their motivation, regulation and the sheer size of the market. Understanding these differences is essential to your development as a forex trader and will only serve to help you in the future. The first thing to understand about the structure of the forex market is the way in which products are traded.
Forex is for the most part, an over the counter OTC market. This means that there is no central exchange through which instruments are traded. When we refer to instruments, we are referring to the different forex products participants use to conduct transactions, whether they be corporate, speculative or hedging.
Spot forex, outright forwards, forex swaps, forex options. When a product is traded OTC it is done so through a market maker. A market maker in forex is effectively a bank or broker that facilitates currency trades by providing buy and sell quotes and then taking orders.
Other commonly traded instruments such as shares and futures are exchange traded products, this means that any transaction involving these instruments is done through an exchange such as the New York Stock Exchange NYSE and London Stock Exchange LSE.
Forex Indicators | Download Free Forex eBooks | Forex PDF | IFC Markets
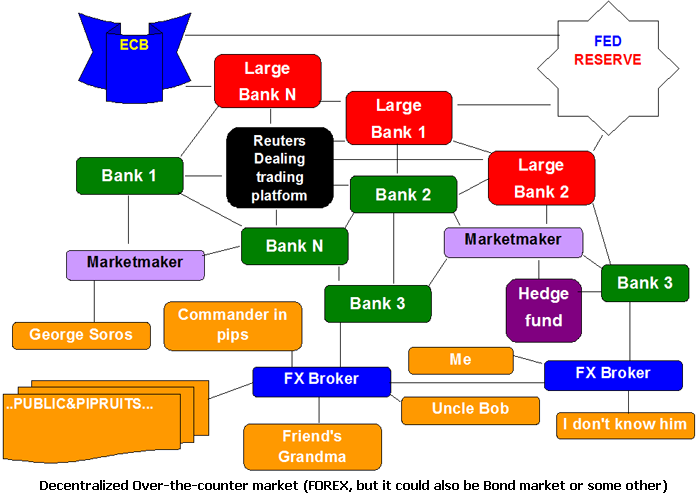
The points below highlight some features of OTC and exchange traded markets. Since there is no central exchange through which to process orders and transactions, a sophisticated network has been established in order to allow participants to communicate and transact.
This network has different levels, each with its own institutions serving different functions within the forex market. The interbank market is essentially a network between larger banks.
This network is made possible through EBS electronic broking services and Reuters spot matching systems. These two applications effectively aggregate the order books of the banks, showing the various bids, offers and amounts that each is willing to transact at.
This allows proper market function to occur by providing sufficient liquidity and efficient processing. The interbank market is only accessible to larger banks with the highest of credit standings, this is to eliminate any counterparty risk and reduce competition.
Forex Market Structure - ybevosapoyud.web.fc2.com
By restricting access to the interbank market the big banks are continuing to maintain their share of forex turnover and thus profits. At the top of the food chain we have the foreign exchange dealers. These are the dealer banks which conduct foreign exchange business for their clients or themselves. The major banks include; Deutsche Bank, UBS, Citigroup, Barclays Capital, RBS, Goldman Sachs, HSBC, Bank of America, JP Morgan, Credit Suisse and Morgan Stanley.
These banks deal with each other on behalf of clients or for themselves, providing much needed liquidity to the market so large transactions tsx stock market predictions corporate or speculative can be facilitated and forex market structure pdf market function can occur.
The dealer banks that form the interbank market are effectively stockyards trading post fort worth market makers of the forex market, they set the prices and manage the volume for the rest of the market to feed off.
On the next level of the forex market we have the market that exists for financial and non-financial participants.

Traditionally the majority of foreign exchange turnover has been the result of international trade flows, this trend has changed in recent years with the majority of turnover being stock market tracker spreadsheet result of capital flows, speculative and hedging activities. This shift reflects the increasing recognition of foreign exchange as a means of generating returns by all market participants, and the need to manage foreign exchange risks through hedging activities.
On the next level we have forex brokers and retail ECNs electronic communications network. Traditionally forex brokers were the intermediary party between buyers and sellers, meaning they facilitated the transaction between the end user and their liquidity provider market maker bank.
For the most part this is still the case today, best binary options with robots and low deposits, some brokers will run a book and trade against their clients.
Brokers and ECNs will usually have an agreement with one or more liquidity providers, through which they can hedge positions on their book and manage any exposure they might have.
A liquidity provider could be any one of the above mentioned major banks, or even another retail broker depending on their needs. In the background of all this we have the central banks.
They are participants in the market to diversify their currency reserves, influence the value of their exchange rate less common nowadays and make international payments on behalf of the government. To do all this the central bank has its own dealers who use a number of larger banks to help facilitate these flows of funds.
Forex Market Structure
Central bank intervention used to be far more common and have greater affect than it has nowadays. Rather than actively participating in the market buying and selling their currency, central banks instead use verbal intervention to affect the value of their currency. To see a full overview of the structure of the fore market please watch the webinar recording below.
Home Education Forex Market Structure. Virgin Islands Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican Venezuela Vietnam Wake Island Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zanzibar Zimbabwe.
Getting Started What is Forex? History of the Forex Market Forex Market Basics Common Order Types Forex Market Structure Spreads and Liquidity What Influences Buying and Selling?
Technical Analysis Fundamental Analysis Metals Trading Forex Terminology. Over The Counter The first thing to understand about the structure of the forex market is the way in which products are traded. OTC Market Made Trading firm is the counterparty Heavy price competition Price and execution quality varies. Exchange Traded Exchange is counterparty to all trades Less price competition Standardised price and execution Regulatory oversight from exchange. The Players At the top of the food chain we have the foreign exchange dealers.
Lesson 6 Next Lesson. Loading nanoRep Excellent Customer Experience. Home Forex Trading Trading Platform Partnerships Education About Us Contact Us Sitemap. IC Markets does not accept applications from residents of the U. The information on this site is not directed at residents in any country or jurisdiction where such distribution or use would be contrary to local law or regulation. Trading Derivatives carries a high level of risk to your capital and you should only trade with money you can afford to lose.
Trading Derivatives may not be suitable for all investors, so please ensure that you fully understand the risks involved, and seek independent advice if necessary. A Product Disclosure Statement PDS can be obtained either from this website or on request from our offices and should be considered before entering into a transaction with us. True ECN accounts offer spreads from 0. Standard account offer spreads from 1 pips with no additional commission charges.
Spreads on CFD indices start at 0.
International Capital Markets holds an Australian financial services licence AFSL to carry on a financial services business in Australia, limited to the financial services covered by its AFSL.
International Capital Markets Pty Ltd. ACN